A finite-volume method for solving parabolic equations on logically Cartesian curved surface meshes
by D. Calhoun and C. HelzelSIAM J. Sci. Comp.,Vol. 31, Issue 6. pp. 4066-4099 (2009)
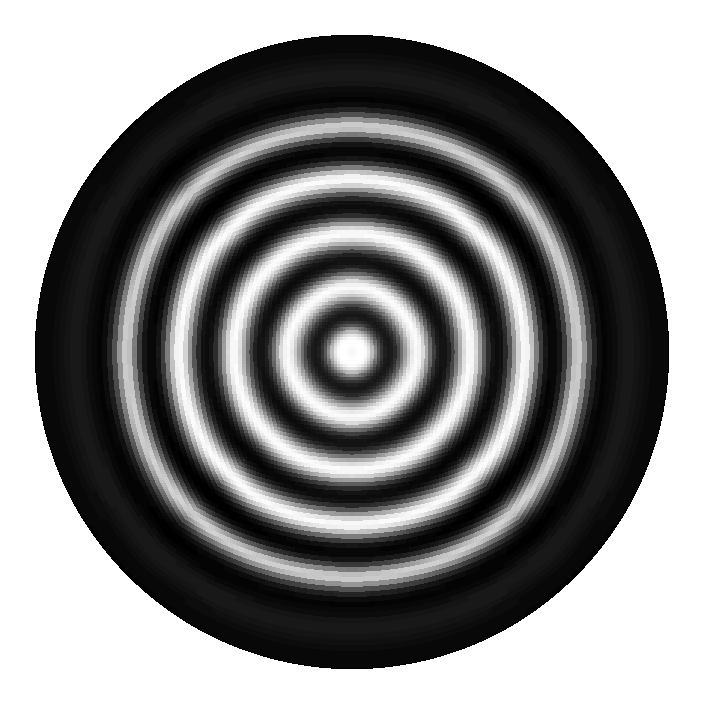
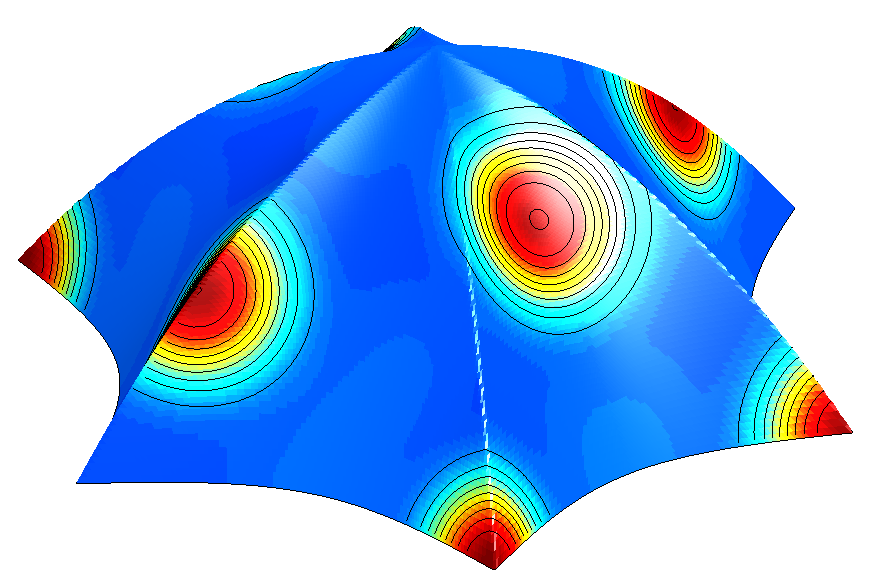
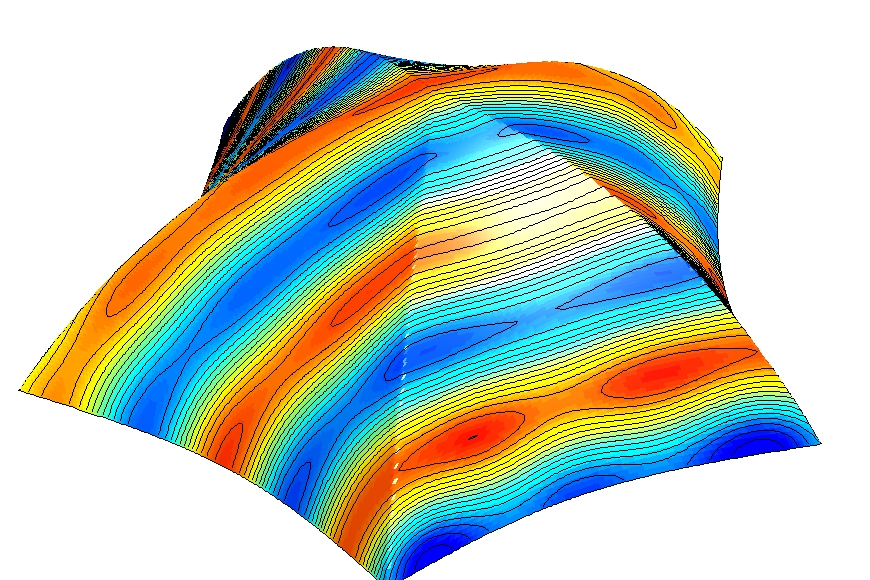
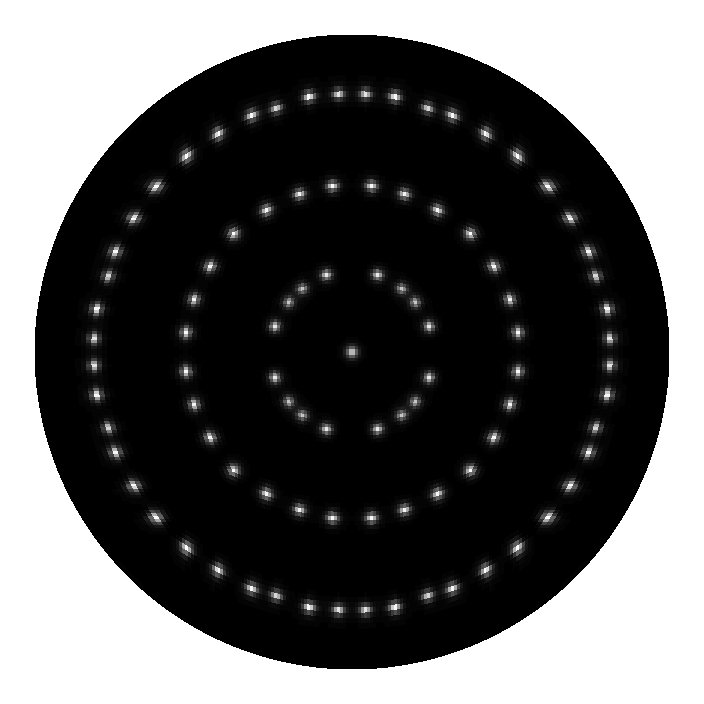
Abstract We present a second-order, finite-volume scheme for the constant-coefficient diffusion equation on curved, parametric surfaces. While our scheme is applicable to general quadrilateral surface meshes based on smooth or piecewise smooth coordinate transformations, our primary motivation for developing the present scheme is to solve diffusion problems on a particular set of circular and spherical meshes introduced in [1] for the discretization of hyperbolic problems. These grids are generated from mappings of a single Cartesian grid and were designed to have nearly uniform cells sizes and avoid the pole singularity associated with polar or spherical grid mappings. The present method for parabolic equations offers several advantages. It does not require analytic metric terms, shows second-order accuracy on our disk and sphere grids, can be easily coupled to existing finite-volume solvers for logically Cartesian meshes and handles general mixed boundary conditions.
Our parabolic scheme should appeal to researchers in the fields of geophysical fluid dynamics, computational biology and any other discipline that requires the solution of parabolic equations on quadrilateral surface meshes. In this article, we present several numerical examples demonstrating the accuracy of the scheme, and then use the scheme to solve advection-reaction-diffusion equations modeling biological pattern formation on surfaces.
Download pre-print : (.pdf)
Recent talk given at the University of Freiburg (2009).
Poster presented at a recent ReaDiLab conference, Orsay, France June 2-5, (2009).
Code which reproduces the results in this paper will be available shortly. Please check back.

Last modified: Mon Nov 30 20:44:19 CET 2009